Edge Worker Deployment¶
Edge Workers can be deployed outside of the central Airflow infrastructure. They are connected to the Airflow API server via HTTP(s). The Edge Worker is a lightweight component that can be deployed on any machine that has outbound HTTP(s) access to the Airflow API server. It allows you to run Airflow tasks on machines that are not part of your main data center, e.g. edge servers. This also allows to deploy only reduced dependencies on the edge worker.
Here are a few imperative requirements for your workers:
airflowneeds to be installed, and the Airflow CLI needs to be in the path. This includes the Task SDK as well as the edge3 provider package.Airflow configuration settings should be homogeneous across the cluster and on the edge site
Operators that are executed on the Edge Worker need to have their dependencies met in that context. Please take a look to the respective provider package documentations
The worker needs to have access to the
DAGS_FOLDER, and you need to synchronize the filesystems by your own means. A common setup would be to store yourDAGS_FOLDERin a Git repository and sync it across machines using Chef, Puppet, Ansible, or whatever you use to configure machines in your environment. If all your boxes have a common mount point, having your pipelines files shared there should work as well
Minimum Airflow configuration settings for the Edge Worker to make it running is:
Section
[api_auth]jwt_secret: A shared secret between workers and the api-server to authenticate (starting from version 3.0.0).
Section
[core]execution_api_server_url: If not set, the base URL fromedge.api_urlwill be used. For example, whenedge.api_urlis set tohttps://your-hostname-and-port/subpath/edge_worker/v1/rpcapi, it will default tohttps://your-hostname-and-port/subpath/execution/(starting from version Airflow version 3.0.0).executor: Executor must be set or added to beairflow.providers.edge3.executors.EdgeExecutorinternal_api_secret_key: An encryption key must be set on api-server and Edge Worker component as shared secret to authenticate traffic. It should be a random string like the fernet key (for versions earlier than 3.0.0 - from Airflow 3.0 and above this is usingapi_auth.jwt_secret).
Section
[edge]api_enabled: Must be set to true. It is disabled intentionally to not expose API endpoint by default. This is the endpoint the worker connects to. In a future release a dedicated API server can be started.api_url: Must be set to the URL which exposes the api endpoint as it is reachable from the worker. Typically this looks likehttps://your-hostname-and-port/edge_worker/v1/rpcapi.
Airflow 3.2 and newer: Once the provider is installed on the central Airflow instance,
the EdgeDBManager is automatically registered via the provider’s built-in db-managers
entry. Airflow’s ProvidersManager discovers it at startup — no manual configuration is needed.
Airflow versions earlier than 3.2: You must explicitly register the EdgeDBManager on the
central Airflow instance so that edge3 database tables (edge_worker, edge_job,
edge_logs) are created and migrated when running airflow db migrate:
Section
[database]external_db_managers: Must includeairflow.providers.edge3.models.db.EdgeDBManager.[database] external_db_managers = airflow.providers.edge3.models.db.EdgeDBManager
Or via environment variable:
export AIRFLOW__DATABASE__EXTERNAL_DB_MANAGERS="airflow.providers.edge3.models.db.EdgeDBManager"
Note
If you are also using
FabAuthManager, include both managers as a comma-separated list:[database] external_db_managers = airflow.providers.fab.auth_manager.models.db.FABDBManager,airflow.providers.edge3.models.db.EdgeDBManager
To create or migrate the edge3 database tables (edge_worker, edge_job, edge_logs),
run on the central Airflow instance:
airflow db migrate
To kick off a worker, you need to setup Airflow and kick off the worker subcommand
airflow edge worker
2025-09-27T12:28:32.954316Z [info ] Starting worker with API endpoint http://localhost:8080/edge_worker/v1/rpcapi
____________ _____________
____ |__( )_________ __/__ /________ __
____ /| |_ /__ ___/_ /_ __ /_ __ \_ | /| / /
___ ___ | / _ / _ __/ _ / / /_/ /_ |/ |/ /
_/_/ |_/_/ /_/ /_/ /_/ \____/____/|__/
____ __ _ __ __
/ __/__/ /__ ____ | | /| / /__ ____/ /_____ ____
/ _// _ / _ / -_) | |/ |/ / _ \/ __/ _/ -_) __/
/___/\_,_/\_, /\__/ |__/|__/\___/_/ /_/\_\\__/_/
/___/
2025-09-27T12:28:33.171525Z [info ] No new job to process
You can also start this worker in the background by running it as a daemonized process. Additionally, you can redirect stdout and stderr to their respective files.
Make sure to set umask in [worker_umask] to set permissions for newly created files by workers.
airflow edge worker -D --stdout edge-worker.o.log --stderr edge-worker.e.log
Your worker should start picking up tasks as soon as they get fired in its direction. To stop a worker running on a machine you can use:
airflow edge stop
It will try to stop the worker gracefully by sending SIGINT signal to main
process as and wait until all running tasks are completed. Also in a console you can use
Ctrl-C to stop the worker.
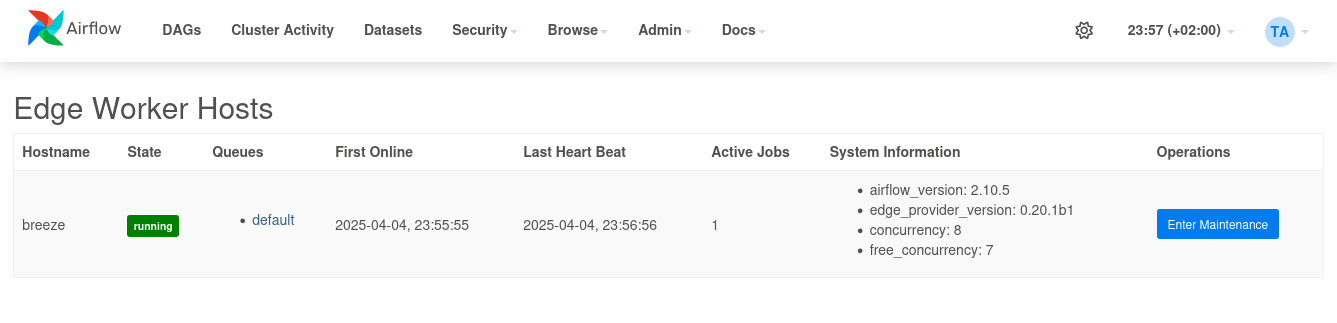
If you want to monitor the remote activity and worker, use the UI plugin which is included in the provider package and install it on the api-server / webserver and use the “Admin” - “Edge Worker Hosts” and “Edge Worker Jobs” pages. (Note: The plugin is not available on Airflow 3.0 UI, it is only in 3.1++)
If you want to check status of the worker via CLI you can use the command
airflow edge status
Some caveats:
Tasks can consume resources. Make sure your worker has enough resources to run
worker_concurrencytasksMake sure that the
pool_slotsof a Tasks matches with theworker_concurrencyof the worker. See also Concurrency slot handling.Queue names are limited to 256 characters
See Modules Management for details on how Python and Airflow manage modules.
Worker Maintenance Mode¶
Sometimes infrastructure needs to be maintained. The Edge Worker provides a maintenance mode to - Stop accepting new tasks - Drain all ongoing work gracefully
Also please note if the worker detects that the Airflow or Edge provider package version is not the same as the one running on the API server, it will stop accepting new tasks and shut down gracefully. This is to prevent running tasks with different versions of the code.
Worker status can be checked via the web UI in the “Admin” - “Edge Worker” page. Maintenance can be set on a per worker basis.
Note
Airflow 3.0 does not support UI plugins. The UI plugin is only available in Airflow 3.1 and newer. Alternatively you can use the CLI commands as described in Worker Maintenance Management CLI.
Worker maintenance can also be triggered via the CLI command on the machine that runs the worker.
airflow edge maintenance --comments "Some comments for the maintenance" on
This will stop the local worker instance from accepting new tasks and will complete running tasks.
If you add the command argument --wait the CLI will wait until all
running tasks are completed before return.
If you want to know the status of you local worker while waiting on maintenance you can use the command
airflow edge status
This will show the status of the local worker instance as JSON and the tasks running on it.
The status and maintenance comments will also be shown in the web UI in the “Admin” - “Edge Worker” page.
The local worker instance can be started to fetch new tasks via the command
airflow edge maintenance off
This will start the worker again and it will start accepting tasks again.
Worker Maintenance Management CLI¶
Besides the CLI command to trigger maintenance on the local worker instance, there are also additional commands to manage the maintenance of all workers in the cluster. These commands can be used to trigger maintenance on all workers in the cluster or to check the status of all workers in the cluster.
These set of commands need database access, and can only be called on the central Airflow instance. The commands are:
airflow edge list-workers: List all workers in the clusterairflow edge remote-edge-worker-request-maintenance: Request a remote edge worker to enter maintenance modeairflow edge remote-edge-worker-update-maintenance-comment: Updates the maintenance comment for a remote edge workerairflow edge remote-edge-worker-exit-maintenance: Request a remote edge worker to exit maintenance modeairflow edge shutdown-remote-edge-worker: Shuts down a remote edge worker gracefullyairflow edge shutdown-all-workers: Request graceful shutdown of all registered edge workersairflow edge remove-remote-edge-worker: Remove a worker instance from the clusterairflow edge add-worker-queues: Add queues to an edge workerairflow edge remove-worker-queues: Remove queues from an edge workerairflow edge set-worker-concurrency: Set the concurrency of a running remote edge worker