HITLOperator (Human-in-the-loop)
Added in version 3.1.
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) functionality allows you to incorporate human decision-making directly into your workflows. This powerful feature enables workflows to pause and wait for human input, making it perfect for approval processes, manual quality checks, and scenarios where human judgment is essential.
In this tutorial, we will explore how to use the HITL operators in workflows and demonstrate how it would look like in Airflow UI.
An HITL Example Dag
Here is what HITL looks like in a Dag. We’ll break it down and dive into it.
/opt/airflow/providers/standard/src/airflow/providers/standard/example_dags/example_hitl_operator.py
class LocalLogNotifier(BaseNotifier):
"""Simple notifier to demonstrate HITL notification without setup any connection."""
template_fields = ("message",)
def __init__(self, message: str) -> None:
self.message = message
def notify(self, context: Context) -> None:
url = HITLOperator.generate_link_to_ui_from_context(
context=context,
base_url="http://localhost:28080",
)
self.log.info(self.message)
self.log.info("Url to respond %s", url)
hitl_request_callback = LocalLogNotifier(
message="""
[HITL]
Subject: {{ task.subject }}
Body: {{ task.body }}
Options: {{ task.options }}
Is Multiple Option: {{ task.multiple }}
Default Options: {{ task.defaults }}
Params: {{ task.params }}
"""
)
hitl_success_callback = LocalLogNotifier(
message="{% set task_id = task.task_id -%}{{ ti.xcom_pull(task_ids=task_id) }}"
)
hitl_failure_callback = LocalLogNotifier(message="Request to response to '{{ task.subject }}' failed")
with DAG(
dag_id="example_hitl_operator",
start_date=pendulum.datetime(2021, 1, 1, tz="UTC"),
catchup=False,
tags=["example", "HITL"],
):
wait_for_input = HITLEntryOperator(
task_id="wait_for_input",
subject="Please provide required information: ",
params={"information": Param("", type="string")},
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
)
wait_for_option = HITLOperator(
task_id="wait_for_option",
subject="Please choose one option to proceed: ",
options=["option 1", "option 2", "option 3"],
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
)
wait_for_multiple_options = HITLOperator(
task_id="wait_for_multiple_options",
subject="Please choose option to proceed: ",
options=["option 4", "option 5", "option 6"],
multiple=True,
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
)
wait_for_default_option = HITLOperator(
task_id="wait_for_default_option",
subject="Please choose option to proceed: ",
options=["option 7", "option 8", "option 9"],
defaults=["option 7"],
execution_timeout=datetime.timedelta(seconds=1),
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
)
valid_input_and_options = ApprovalOperator(
task_id="valid_input_and_options",
subject="Are the following input and options valid?",
body="""
Input: {{ ti.xcom_pull(task_ids='wait_for_input')["params_input"]["information"] }}
Option: {{ ti.xcom_pull(task_ids='wait_for_option')["chosen_options"] }}
Multiple Options: {{ ti.xcom_pull(task_ids='wait_for_multiple_options')["chosen_options"] }}
Timeout Option: {{ ti.xcom_pull(task_ids='wait_for_default_option')["chosen_options"] }}
""",
defaults="Reject",
execution_timeout=datetime.timedelta(minutes=5),
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
assigned_users=[{"id": "1", "name": "airflow"}, {"id": "admin", "name": "admin"}],
)
choose_a_branch_to_run = HITLBranchOperator(
task_id="choose_a_branch_to_run",
subject="You're now allowed to proceeded. Please choose one task to run: ",
options=["task_1", "task_2", "task_3"],
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
)
@task
def task_1(): ...
@task
def task_2(): ...
@task
def task_3(): ...
(
[wait_for_input, wait_for_option, wait_for_default_option, wait_for_multiple_options]
>> valid_input_and_options
>> choose_a_branch_to_run
>> [task_1(), task_2(), task_3()]
)
Input Provision
Users can provide input using params that is used for subsequent tasks. This is useful for workflows involving human guidance within large language model (LLM) workflows.
/opt/airflow/providers/standard/src/airflow/providers/standard/example_dags/example_hitl_operator.py
wait_for_input = HITLEntryOperator(
task_id="wait_for_input",
subject="Please provide required information: ",
params={"information": Param("", type="string")},
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
)
You can click the task and find the Required Actions tab in the details panel.
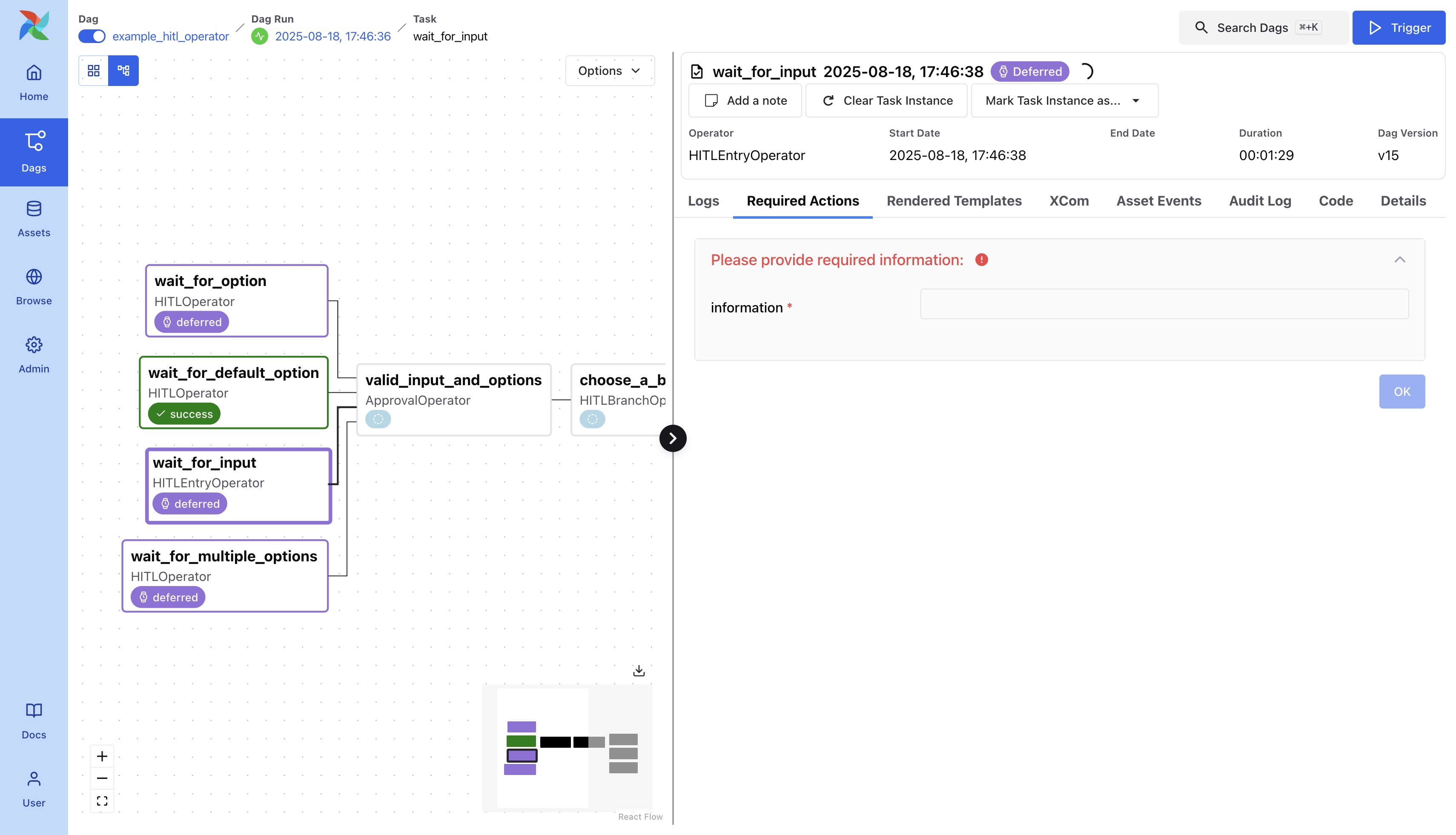
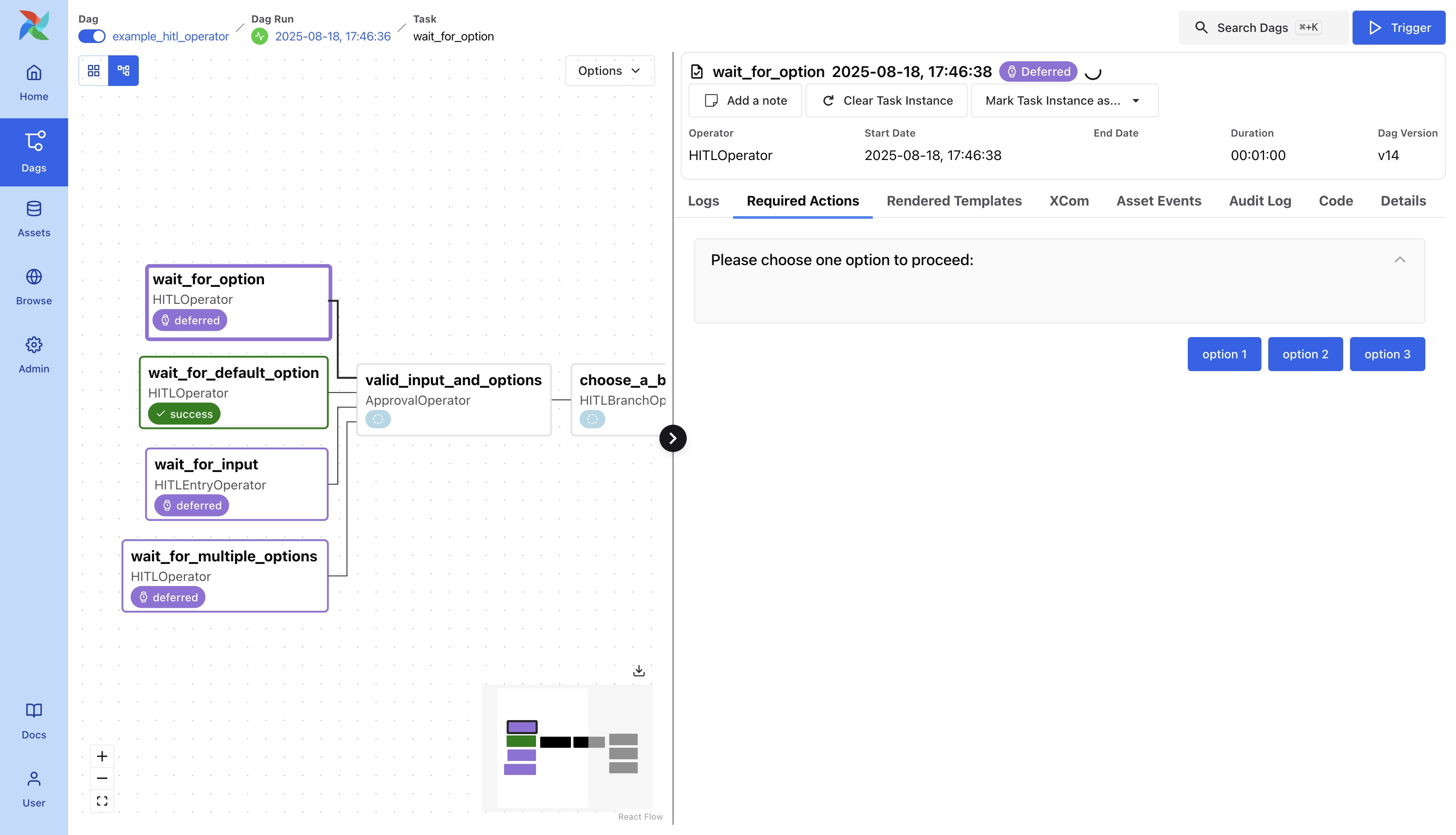
Option Selection
Input can be provided in the form of options. Users can select one of the available options, which can be used to direct the workflow.
/opt/airflow/providers/standard/src/airflow/providers/standard/example_dags/example_hitl_operator.py
wait_for_option = HITLOperator(
task_id="wait_for_option",
subject="Please choose one option to proceed: ",
options=["option 1", "option 2", "option 3"],
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
)
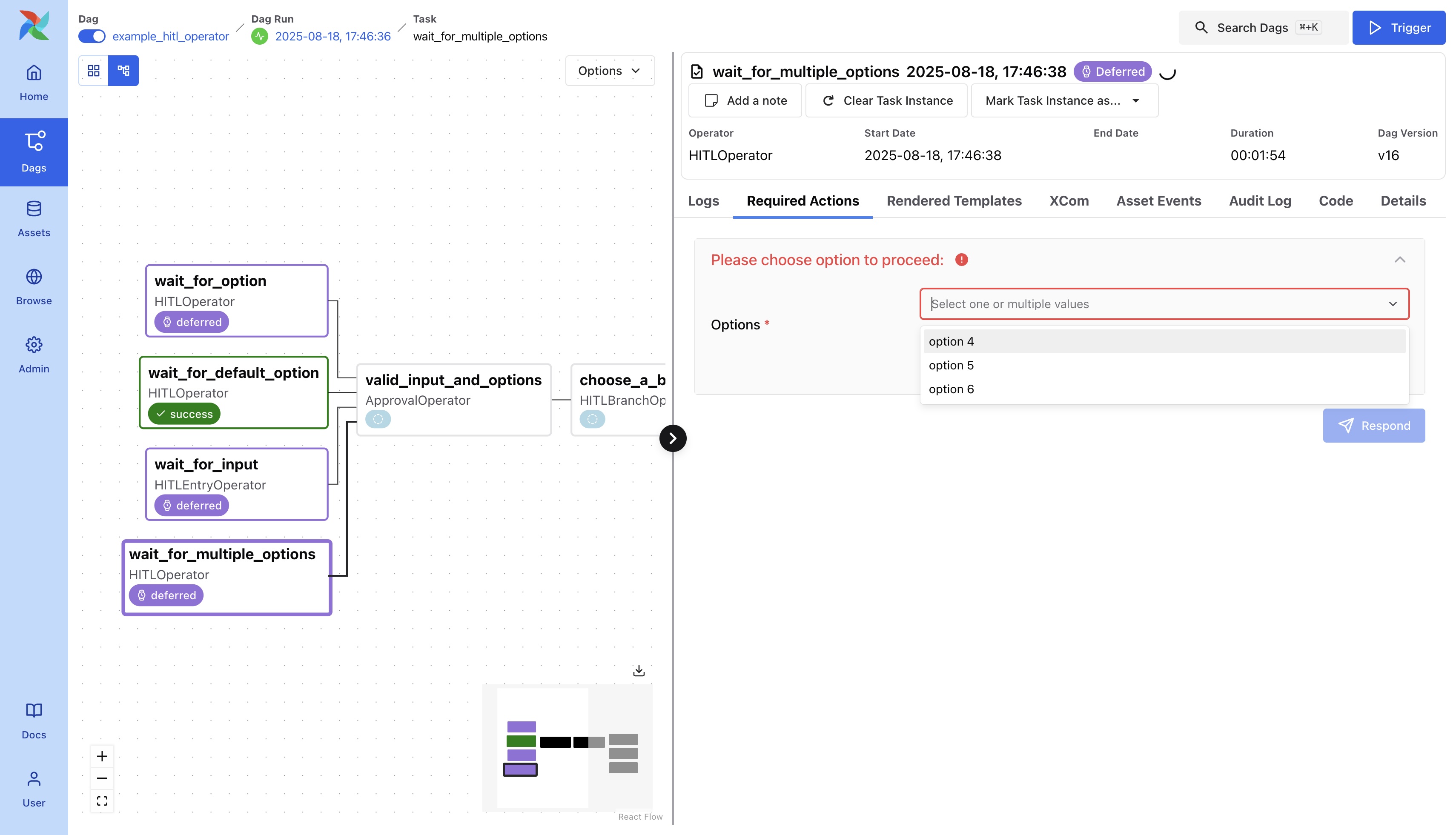
Multiple options are also allowed.
/opt/airflow/providers/standard/src/airflow/providers/standard/example_dags/example_hitl_operator.py
wait_for_multiple_options = HITLOperator(
task_id="wait_for_multiple_options",
subject="Please choose option to proceed: ",
options=["option 4", "option 5", "option 6"],
multiple=True,
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
)
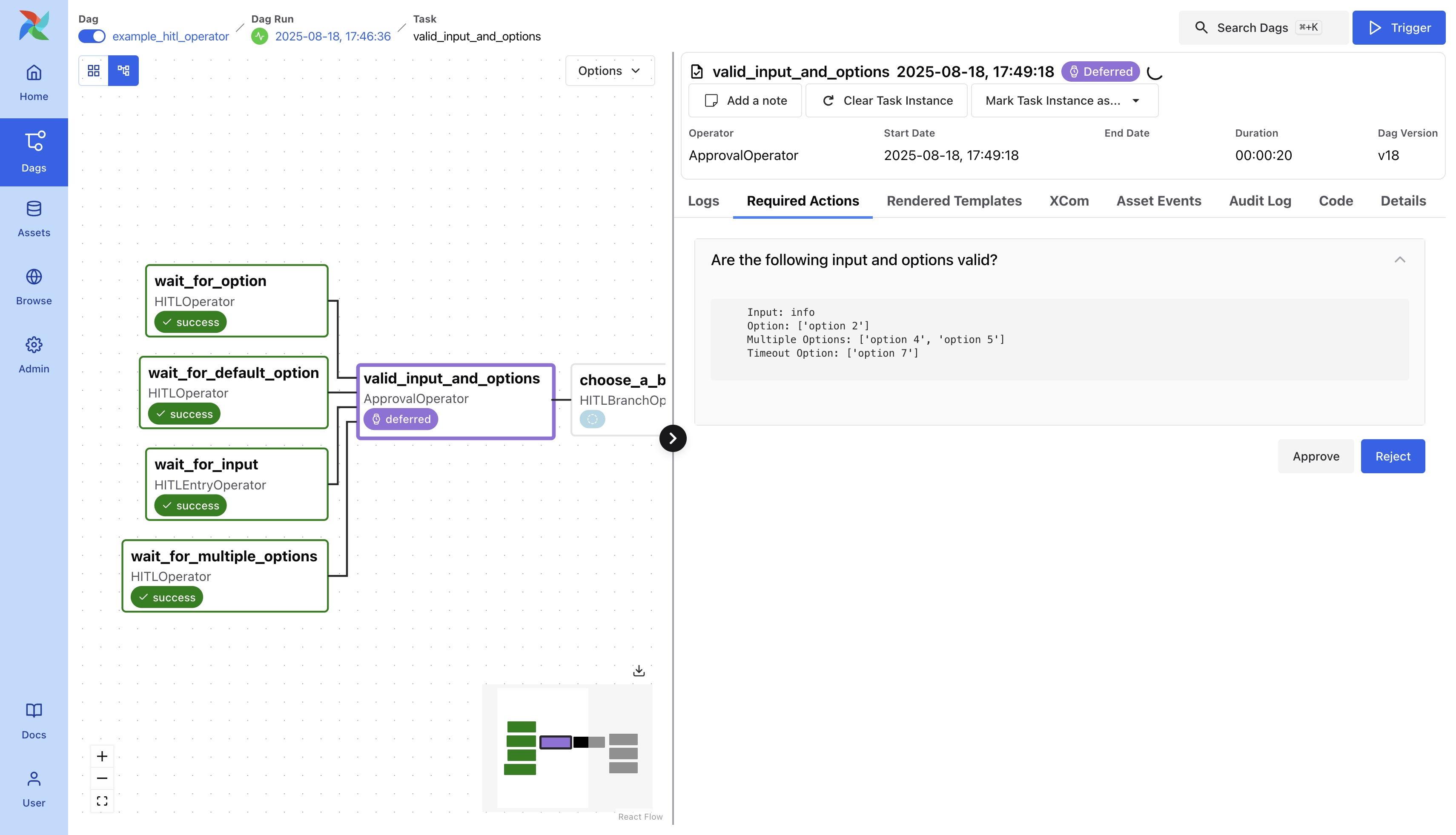
Approval or Rejection
A specialized form of option selection, which has only ‘Approval’ and ‘Rejection’ as options.
You can also set the assigned_users to restrict the users allowed to respond for a HITL operator.
It should be a list of user ids and user names (both needed) (e.g., [{"id": "1", "name": "user1"}, {"id": "2", "name": "user2"}].
ONLY the users within this list will be allowed to respond.
/opt/airflow/providers/standard/src/airflow/providers/standard/example_dags/example_hitl_operator.py
valid_input_and_options = ApprovalOperator(
task_id="valid_input_and_options",
subject="Are the following input and options valid?",
body="""
Input: {{ ti.xcom_pull(task_ids='wait_for_input')["params_input"]["information"] }}
Option: {{ ti.xcom_pull(task_ids='wait_for_option')["chosen_options"] }}
Multiple Options: {{ ti.xcom_pull(task_ids='wait_for_multiple_options')["chosen_options"] }}
Timeout Option: {{ ti.xcom_pull(task_ids='wait_for_default_option')["chosen_options"] }}
""",
defaults="Reject",
execution_timeout=datetime.timedelta(minutes=5),
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
assigned_users=[{"id": "1", "name": "airflow"}, {"id": "admin", "name": "admin"}],
)
As you can see in the body of this code snippet, you can use XComs to get information provided by the user.
Branch Selection
Users can choose which branches to follow within the Dag. This is commonly applied in scenarios such as content moderation, where human judgment is sometimes required.
This is like option selection, but the option needs to be a task. And remember to specify their relationship in the workflow.
/opt/airflow/providers/standard/src/airflow/providers/standard/example_dags/example_hitl_operator.py
choose_a_branch_to_run = HITLBranchOperator(
task_id="choose_a_branch_to_run",
subject="You're now allowed to proceeded. Please choose one task to run: ",
options=["task_1", "task_2", "task_3"],
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
)
/opt/airflow/providers/standard/src/airflow/providers/standard/example_dags/example_hitl_operator.py
@task
def task_1(): ...
@task
def task_2(): ...
@task
def task_3(): ...
(
[wait_for_input, wait_for_option, wait_for_default_option, wait_for_multiple_options]
>> valid_input_and_options
>> choose_a_branch_to_run
>> [task_1(), task_2(), task_3()]
)
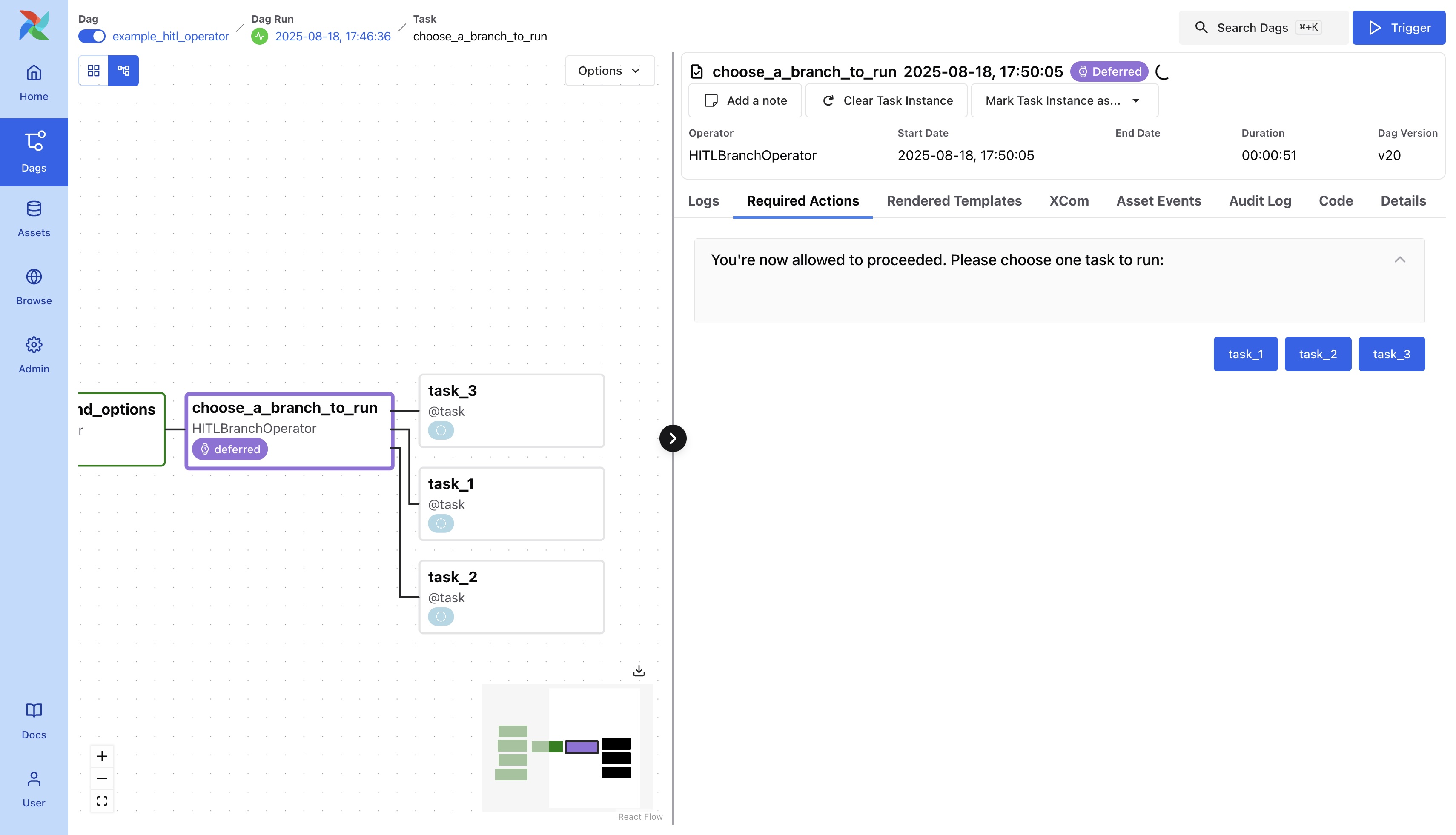
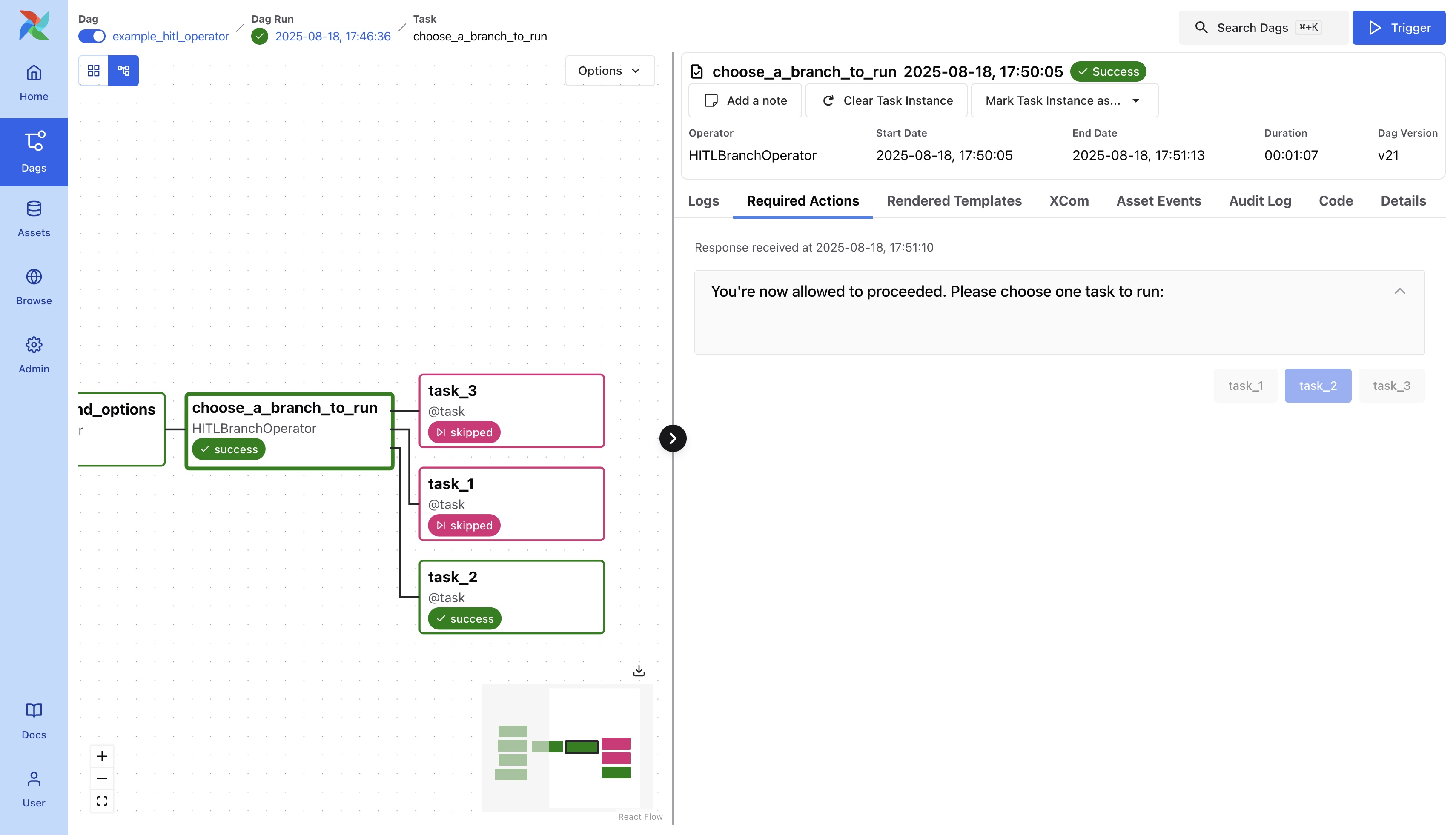
After the branch is chosen, the workflow will proceed along the selected path.
Notifiers
A notifier is a callback mechanism for handling HITL events, such as when a task is waiting for human input, succeeds, or fails.
The example uses the LocalLogNotifier, which logs messages for demonstration purposes.
The method HITLOperator.generate_link_to_ui_from_context can be used to generate a direct link to the UI page where the user should respond. It accepts four arguments:
context– automatically passed tonotifyby the notifierbase_url– (optional) the base URL of the Airflow UI; if not provided,api.base_urlin the configuration will be usedoptions– (optional) pre-selected options for the UI pageparams_inputs– (optional) pre-loaded inputs for the UI page
This makes it easy to include actionable links in notifications or logs. You can also implement your own notifier to provide different functionalities. For more details, please refer to Creating a notifier and Notifications.
In the example Dag, the notifier is defined as follows:
/opt/airflow/providers/standard/src/airflow/providers/standard/example_dags/example_hitl_operator.py
class LocalLogNotifier(BaseNotifier):
"""Simple notifier to demonstrate HITL notification without setup any connection."""
template_fields = ("message",)
def __init__(self, message: str) -> None:
self.message = message
def notify(self, context: Context) -> None:
url = HITLOperator.generate_link_to_ui_from_context(
context=context,
base_url="http://localhost:28080",
)
self.log.info(self.message)
self.log.info("Url to respond %s", url)
hitl_request_callback = LocalLogNotifier(
message="""
[HITL]
Subject: {{ task.subject }}
Body: {{ task.body }}
Options: {{ task.options }}
Is Multiple Option: {{ task.multiple }}
Default Options: {{ task.defaults }}
Params: {{ task.params }}
"""
)
hitl_success_callback = LocalLogNotifier(
message="{% set task_id = task.task_id -%}{{ ti.xcom_pull(task_ids=task_id) }}"
)
hitl_failure_callback = LocalLogNotifier(message="Request to response to '{{ task.subject }}' failed")
You can pass a list of notifiers to HITL operators using the notifiers argument as follows.
When the operator creates an HITL request that is waiting for a human response, the notify method will be called with a single argument, context.
/opt/airflow/providers/standard/src/airflow/providers/standard/example_dags/example_hitl_operator.py
wait_for_input = HITLEntryOperator(
task_id="wait_for_input",
subject="Please provide required information: ",
params={"information": Param("", type="string")},
notifiers=[hitl_request_callback],
on_success_callback=hitl_success_callback,
on_failure_callback=hitl_failure_callback,
)
Benefits and Common Use Cases
HITL functionality is valuable in large language model (LLM) workflows, where human-provided guidance can be essential for achieving better results. It is also highly beneficial in enterprise data pipelines, where human validation can complement and enhance automated processes.